Unlocking Potential: What 3D Printer Is Used For in Today’s World?
Originally posted on October 19, 2023 @ 8:27 am
Curious about the uses of a 3D printer? Discover the revolutionary technology of 3D printing and its wide range of potential applications.
From rapid prototyping to customized creations, discover how a 3D printer is used in revolutionizing industries, additive manufacturing processes, crafting intricate designs, and transforming ideas into tangible reality.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, entrepreneur, or creative mind, this comprehensive guide reveals the limitless possibilities. Stay ahead of the curve and harness the power of 3D printing to innovate, create, and redefine the future. Read on to explore the possibilities.
Key Takeaways – What Are The Uses Of 3D Printers
The 3D printer is used for
- From tooling aids to functional prototypes and even end-use parts, their applications vary widely. In construction, 3D printing involves techniques like additive welding and powder bonding (reactive, polymer, and sintering).
- Aerospace and defense companies use 3D printing extensively for lightweight parts.
- Medical and dental fields also use 3D printing.
- These innovations redefine production, enabling swift prototyping and efficient creation of intricate, customized components across diverse sectors.
What Are The Uses Of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing In The Future?
Aerospace Industry for Rapid Prototyping
3D printers have revolutionized the aerospace and defense industries by offering unparalleled versatility and efficiency. In aerospace, they enable prototyping, allowing engineers to iterate designs swiftly and test various configurations.
Customized components, crucial for aircraft, are produced with precision, reducing weight and improving performance. 3D printing plays a pivotal role in tooling aids, and crafting specialized fixtures for assembly and additive manufacturing processes.
Maintenance and repair operations benefit immensely as 3D printers generate replacement parts swiftly, minimizing downtime. Moreover, the technology aids in optimizing designs for lightweight yet structurally robust parts, essential for aerospace companies’ applications.
Defense
In defense, 3D printers are indispensable for creating intricate components for defense equipment. They facilitate the rapid production of complex geometries and innovative materials, enhancing the durability and functionality of military-grade equipment.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are developed with rapid prototyping business models, allowing for the swift iteration of designs, resulting in agile and high-performance drones.
Furthermore, 3D printing streamlines the supply chain by enabling on-demand production, reducing costs associated with inventories.
In essence, 3D printing in aerospace and defense ensures quicker innovation, cost efficiency, and adaptability, cementing its vital role in shaping the future of these industries.
Spare and Replacement Parts
3D printers have revolutionized the production of spare and replacement parts across various industries. With this technology, businesses can manufacture intricate components on demand, reducing the need for large inventories. This not only saves costs but also minimizes downtime, ensuring swift repairs and maintenance.
Whether it’s an automotive part, a specialized tool, or a component in an additive manufacturing machine, 3D printers enable precise replication. Moreover, they facilitate the production of discontinued or rare parts, extending the lifespan of older equipment.
The ability to create customized, high-quality spare parts efficiently has made 3D printing a game-changer in ensuring uninterrupted operations for businesses worldwide.
Design
3D printing is sure to reshape the landscape of design by offering unprecedented freedom and efficiency. Designers can transform their digital concepts into tangible prototypes rapidly and affordably, enabling iterative refinement.
Complex geometries and intricate details, once challenging to produce, are now achievable with precision. This technology fosters creativity, allowing designers to experiment without traditional additive manufacturing constraints.
Additionally, 3D printing facilitates customized solutions, tailoring designs to specific needs.
From product prototypes and architectural models to full medical devices and implants, this transformative technology accelerates the design process, encourages innovation, and bridges the gap between imagination and reality.
As a result, it empowers designers across industries to explore, innovate, and bring their visions to life with unparalleled flexibility and speed.
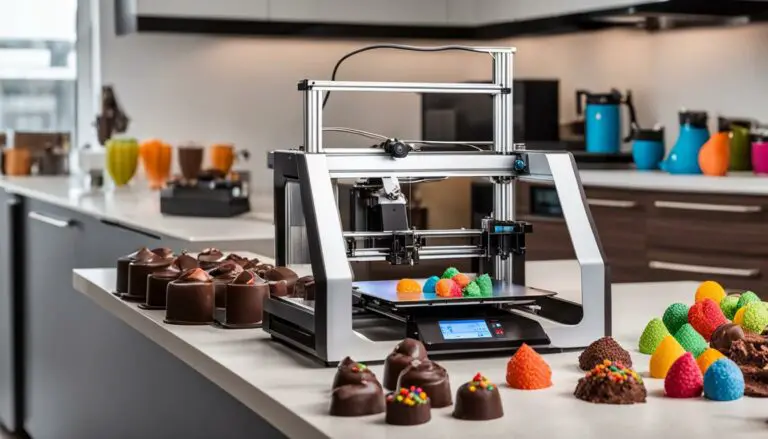
Food Printing
3D printers have extended their innovation into the culinary world, introducing eatables printing technology in the consumer goods industry.
By using edible ingredients, these printers craft intricate and customized food items, from chocolates and pastries to intricate garnishes in the final manufacture.
This revolution in gastronomy promises not only aesthetically pleasing dishes but also opens new avenues for culinary creativity and personalization.
CUPRA Racing
CUPRA and SEAT, prominent names in motorsports, leverage 3D printing technology extensively.
They utilize computer-aided design and additive manufacturing with product development processes for quick prototyping, creating lightweight components, and customizing parts for their race cars.
This innovative approach enhances aerodynamics and performance, giving them a competitive edge on the track while showcasing the versatility and efficiency of 3D printing in the world of racing.
Medical and Dental Appliances
In the medical and dental industry fields, 3D printers have revolutionized patient care and tissue engineering applications. Dentists utilize 3D printing for precise molds, crowns, bridges, and aligners tailored to individual patient needs as just one example.
n healthcare, the technology enables the rapid manufacturing of custom prosthetics, orthopedic implants, and patient-specific models for surgical planning using computer-aided design.
Bioprinting, a cutting-edge application and the latest digital trends, involves creating living tissues for research and potential transplantation. 3D printing also aids in anatomical models, allowing surgeons to practice complex procedures before operations.
This technology enhances treatment accuracy, reduces costs, and significantly improves patient outcomes, marking a transformative shift in the medical and dental industries’ approach to personalized and efficient care.
Other Manufacturing Process Industrial Applications
Beyond prototyping, 3D printers find diverse industrial applications. In the healthcare industry, they create custom implants and prosthetics.
Automotive industries use them for rapid manufacturing custom tooling and customized components. 3D printing aids jewelry design, enabling intricate creations.
It’s vital in architecture for detailed models. Additionally, it’s integral in aerospace for lightweight, complex parts, showcasing its vast manufacturing industry utility.
Check Out – Other Types of Printers and Their Uses
What Are the 5 Benefits Of 3D Printing over Traditional Manufacturing Methods?
Innovative Prototyping
3D printing accelerates the prototyping process by swiftly translating digital designs into physical objects. This rapid iteration fosters innovation, allowing designers and engineers to refine concepts effectively and cost-efficiently.
Customization and Personalization
One example of the significant benefits of 3D printing is its ability to create customized, tailor-made products. From personalized medical implants to individually designed consumer goods, this technology empowers businesses and individuals to meet specific needs and preferences.
Complex Geometries Made Easy
Traditional manufacturing methods often struggle with intricate designs.
3D printing excels in creating complex shape geometries and intricate structures that are challenging or impossible to produce with conventional techniques, opening up new possibilities in product design custom additive manufacturing, and architecture.
Reduced Waste and Sustainable Production
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, which means it adds raw material layer by layer, reducing waste significantly compared to subtractive and traditional methods. Additionally, it enables localized production, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and storage.
Cost-Effective Low-Volume Production
For small-scale production runs, 3D printing eliminates the need for costly molds or tooling. This cost efficiency makes it an attractive option for on-demand additive manufacturing, allowing businesses to produce limited quantities economically and reducing inventory costs and waste.
Is It Expensive To 3D Print? Is It Worth It To Buy A 3D Printer?
Cost
The cost of 3D printing varies based on factors like material, printer type, and the complexity of the design.
Basic desktop printers are affordable for enthusiasts and small businesses, but high-end industrial printers and specialized materials can be costly. Moreover, recurring expenses include filaments and maintenance.
While initial investments vary, the technology’s accessibility has improved, making it more affordable overall.
It may be possible to save money on successfully printed virtual reality objects in future supply chains. For simple projects and prototypes, 3D printing can be cost-effective, but intricate or large-scale production may incur significant expenses.
Related Content – How Much is a Printer?
Is It Worthwhile?
Investing in a 3D printer can be immensely worthwhile, depending on your needs and interests. For hobbyists, designers, and educators, it offers an unparalleled platform for creativity, enabling the production of intricate models, prototypes, and personalized items.
Businesses benefit from rapid prototyping, streamlined additive manufacturing processes, and on-demand production of spare parts, reducing costs and enhancing efficiency.
In the medical field, 3D printing revolutionizes patient-specific devices, body parts, treatments, and research.
However, it’s essential to consider the learning curve, maintenance, and material costs. For enthusiasts willing to explore its potential and businesses aiming to innovate and optimize production, a 3D printer can be a highly valuable and transformative investment.
What Is 3D Printing Used For Examples?
3D printing is employed across diverse sectors for numerous applications. In healthcare, it creates custom prosthetics and implants, for medical device manufacturers while in aerospace, it manufactures lightweight components.
Architects use 3D printing for intricate models, and automotive industries produce customized parts swiftly. Additionally, it aids in crafting jewelry designs and artistic sculptures.
Engineers use 3D printing for rapid prototypes on the factory floor and tooling aids, enhancing additive manufacturing efficiency. From educational purposes to industrial innovations, 3D printing’s versatility is showcased through its wide array of applications.
What Industry Uses 3D Printing The Most? What Is 3D Printing Most Commonly Used For?
The automotive industry is a leading adopter of 3D printing in just a few days, utilizing it for rapid prototyping, additive manufacturing custom components, and even producing entire vehicles in remote locations with mass customization.
Additionally, aerospace and international space stations heavily rely on 3D printing for lightweight, complex aircraft parts. The healthcare and medical industry also utilizes technology for creating personalized prosthetics or to create patient-specific devices, implants, and anatomical models. Printing food can help in space and astronauts.
Education benefits from 3D printing in classrooms for teaching complex concepts visually. Architectural firms use it for detailed scale models. Furthermore, 3D printing is widely employed in product design, fashion, and entertainment, showcasing its versatility.
Its applications span from prototypes to end-use parts, making it a pivotal technology across diverse sectors.
How Is 3D Printing Used In Real Life?
3D printing has transformative real-life applications across industries. In healthcare, it produces patient-specific implants and prosthetics.
- Architects use printed objects for detailed scale models of spare parts, while automotive sectors create custom components.
- Additive Manufacturing relies on 3D printing for rapid prototyping, creating spare parts and tooling aids, and streamlining production.
- Educators use it to enhance learning experiences through tangible models. In aerospace, intricate and lightweight parts are 3D printed for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Even fashion designers use the technology for avant-garde creations. From medical advancements to educational tools and cutting-edge design, 3D printing plays a pivotal role in shaping our real-world applications and experiences.
What Are 5 Different Types Of 3D Printing?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM or fused filament fabrication is the most common 3D printing method and among the new technologies of the production process, where thermoplastic filaments are melted and layered to create objects. It’s widely used due to its affordability and versatility in other industries.
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA uses liquid resin cured by ultraviolet light to create precise and detailed objects. It’s ideal for intricate designs and high-resolution prototypes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS or selective laser sintering employs a laser to sinter metal powder materials, usually polymers or metals, layer by layer. It is the dental industry that is renowned for producing durable, functional parts and electronic devices with complex geometries.
There is also a direct metal laser sintering or DMLS.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA, DLP digital technologies use light to cure liquid resin. It’s faster than SLA as entire layers are cured simultaneously, making it suitable for rapid prototyping and small-scale production.
You can also have powder bed fusion or PBF which is one of the new business models in the business world.
PolyJet Printing
PolyJet technology jets layers of liquid photopolymer onto a build tray, which are then cured instantly with UV light. It’s known for its high precision, enabling multi-material, multi-color prints ideal for detailed prototypes and artistic models.
What Products Do You Need With A 3D Printer?
To maximize the potential of a 3D printer, several essential products are required.
- Metal Filaments – Firstly, quality filaments in various materials like PLA, ABS, or PETG are essential, as they form the basis of 3D prints.
- Build surfaces– these include glass beds or adhesive sheets, ensuring proper adhesion during printing.
- An efficient slicer software – computer-aided manufacturing software is crucial for converting 3D models into printable instructions.
- Calibration tools- these consist of leveling kits and calipers and are necessary for precise prints.
- Maintenance tools, like cleaning brushes and lubricants, ensure the printer’s longevity.
- Safety equipment or personal protective equipment such as gloves and masks might be needed, especially when handling certain materials.
- Additionally, having a stable and level surface to place the 3D printer is essential to prevent vibrations during printing, ensuring high-quality results.
Are 3D Printers Useful At Home? What Do You Use A 3D Printer For At Home?
Absolutely, 3D printers are incredibly useful at home. They enable enthusiasts, hobbyists, and DIYers to bring their creative ideas to life, whether it’s crafting custom phone cases, personalized home decor, or intricate toys for children.
Homeowners can print replacement parts for appliances, new medical devices in less than an hour, etc. avoiding costly replacements. It’s also a boon for educators, aiding in visually engaging lessons with 3D-printed teaching aids to give great examples to students.
Additionally, 3D printers support educational projects, helping students understand complex concepts through tangible models. For tech enthusiasts, it’s a gateway to experimenting with prototypes of spare parts and inventions.
Furthermore, the technology fosters a sense of innovation and learning within the comfort of one’s home, making 3D printers valuable tools for various household needs and creative pursuits.
What Is the Disadvantage Of Using 3D Printing For Homes?
One disadvantage of using 3D printing for homes is the high cost. Also, there is a limited range of materials available for consumer-grade printers. While industrial printers can use diverse materials, home 3D printers primarily work with plastic and carbon fiber.
This limitation restricts the types of products that can be printed in terms of durability and functionality.
Additionally, the printing process can be time-consuming for larger or intricate items, requiring significant patience.
Finally, there’s a learning curve associated with operating and troubleshooting 3D printers, since it is constantly expanding too which might be a challenge for some users.
How Much Does A 3d Printer Cost For Home Use?
The cost of 3D printers for home use varies widely, ranging from around $200 to $800 for entry-level desktop models suitable for beginners and enthusiasts. Mid-range printers with more features and larger print volumes can cost between $800 and $2000.
High-end or professional-grade 3D printers, equipped with advanced capabilities, can range from $2000 to $5000 or more. The price depends on factors like build size, print quality, and additional features like dual extruders or heated beds.
Additionally, ongoing expenses include filament, maintenance, and potential upgrades in desired objects, which users should consider when budgeting for home 3D printing.
Why 3D Printers Are Not Used At Home?
While 3D printers have gained popularity, not every household uses them due to several reasons. First, the initial cost can be a barrier, especially for high-quality, feature-rich models.
Additionally, the learning curve associated with operating and troubleshooting 3D printers might deter some users.
Limited awareness about the technology’s practical applications at home and the perception of complexity could also contribute. Moreover, the availability of ready-made products and the convenience of online shopping often outweigh the effort and time required for 3D printing.
As technology advances in directed energy deposition and becomes more user-friendly, wider adoption in homes is likely, but for now, these factors limit its common use.
What Materials Can Be 3d Printed At Home?
At home, 3D printers primarily work with various thermoplastic filaments. Common materials include
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) is known for its ease of use, low cost, and environmental friendliness.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is durable and impact-resistant, suitable for functional spare parts.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) offers both strength and flexibility, making it versatile for different applications of on-demand manufacturing.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a flexible filament often used for phone cases and rubber-like objects.
- Specialty filaments like woodfill, metal-filled, and carbon fiber-infused materials provide unique textures and enhanced properties.
However, it’s crucial to note that different printers require specific materials, and not all materials are suitable for every printer. As technology advances, more materials are becoming accessible for home 3D printing, broadening the possibilities for creative and practical applications.
Can I Make Money 3D Printing?
Yes. Absolutely! 3D printing offers various avenues to generate income, making it a viable business venture.
Custom Prototyping Services
Offer prototyping services to inventors, product designers, and businesses. 3D printing allows you to create prototypes swiftly and cost-effectively, attracting clients in need of tangible proof of concepts.
Customized Products
Create a niche in personalized items, such as custom phone cases, medical devices, home décor, or personalized gifts. Cater to specific customer requests, leveraging 3D printing’s ability to create unique and intricate designs.
Small-Scale Manufacturing
Produce and sell small batches of specialized or niche products. 3D printing enables on-demand additive manufacturing or custom manufacturing of medical devices, reducing storage costs and allowing you to create tools that cater to niche markets that might not be economically viable for large-scale manufacturers.
3D Scanning and Printing Services
Combine 3D scanning technology with printing services. Offer services to individuals or businesses looking to replicate or modify existing objects, artifacts, or heirlooms.
Educational Workshops and Tutorials
Share your expertise by conducting workshops and tutorials. Many people are interested in learning 3D printing but lack the knowledge. Offer training sessions, both online and offline, covering basics, design software, and troubleshooting.
Online Marketplaces
Sell your 3D-printed items on online platforms like Etsy, and Shapeways, or even create your e-commerce store. Unique and well-designed products attract buyers interested in supporting individual artisans.
Specialized Services for Industries
Collaborate with specific industries, such as healthcare or aerospace, to provide specialized 3D printing services for their unique needs, like customized medical models or aerospace prototypes.
Maintenance and Repair Services
Offer maintenance and repair services for 3D printers. Many individuals and businesses face challenges in operating and troubleshooting their printers. Providing technical support can be a lucrative business opportunity.
What Am I Not Allowed To 3D Print? Can You 3D Print A Gun?
Legal and Ethical Boundaries
While 3D printing technology offers incredible possibilities, there are legal and ethical constraints that individuals must adhere to. While 3D printing offers immense creative freedom, it is vital to operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
Respecting intellectual property, privacy, and societal norms ensures that the technology is used responsibly, positively contributing to innovation without causing harm or violating the law.
Weapons and Firearms
In many jurisdictions, it is illegal and highly unethical to 3D print firearms or weapon components. This includes guns, ammunition, and accessories like silencers. Printing such items can lead to severe legal consequences, including imprisonment.
Legislation and regulations regarding 3D-printed firearms vary worldwide, and attempting to print a weapon without proper authorization is a serious offense.
Counterfeit Items
Creating counterfeit products, such as replica branded goods or copyrighted items, without permission infringes upon intellectual property rights.
This is both ethically questionable and illegal. Companies invest heavily in research, design, and development, and counterfeiting undermines their efforts and profits.
Harmful or Offensive Objects
3D printing harmful or offensive items, like dangerous gadgets or objects promoting hate speech, violence, or discrimination, is not only socially unacceptable but can also lead to legal repercussions.
Responsible and ethical use of 3D printing technology is essential to maintaining a positive impact on society.
Patented Products
Reproducing patented products without the patent holder’s consent is a violation of intellectual property laws. Even if you can 3D print an item, it is crucial to respect patents and not infringe upon the rights of the patent owner.
Items That Violate Privacy
Creating objects like hidden cameras or spying devices that invade someone’s privacy is not only morally wrong but also illegal. Respect for privacy is essential, and 3D printing should not be used to compromise it.
Drugs and Paraphernalia
3D Printing drug-related items or objects associated with drug use, such as bongs or pipes, is generally against the law and socially discouraged. It’s important to adhere to local laws and medical industry regulations regarding drug-related paraphernalia.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of a 3D printer?
The main purpose of a 3D printer is to create three-dimensional objects from digital files. It achieves this by layering materials, such as plastics or metals, to build the object layer by layer based on the provided design.
What is the main use of 3D printing?
The main use of 3D printing is to rapidly prototype, customize, and manufacture various objects and parts across diverse industries, ranging from healthcare and aerospace to automotive and consumer goods. It enables efficient production of complex, customized, and innovative designs, revolutionizing additive manufacturing and design processes.
What can I make with a 3D printer? What can I use my 3D printer for?
With a 3D printer, you can create a wide range of items including prototypes, customized products, home decor, educational models, toys, jewelry, replacement parts, and more.
The versatility of 3D printing allows you to bring your ideas to life, from practical solutions to artistic creations, limited only by your imagination and the capabilities of the printer and materials you have.
Can I use a 3D printer in my house?
Yes, you can use a 3D printer in your house. Many desktop 3D printers are designed for home use, providing a convenient way to create various objects and prototypes. However, it’s essential to consider safety precautions, proper ventilation, and the noise level of the printer.
Additionally, understanding the basics of 3D printing, such as calibrating the printer and choosing suitable materials, is crucial for successful and safe operation at home.
What is the most common use of a 3D printer?
The most common use of a 3D printer is rapid prototyping. It allows businesses and individuals to quickly create physical prototypes of products, designs, and concepts.
This iterative process enables testing, refining, and perfecting ideas before mass production, saving time and resources in product development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the myriad benefits and uses of 3D printing have transformed industries and empowered creative minds. Its ability to rapidly prototype, customize, and innovate has revolutionized additive manufacturing, the automotive industry, healthcare, education, and more.
By fostering efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling intricate designs, 3D printers have become indispensable tools for businesses and individuals alike.
The technology’s continual evolution promises even greater possibilities than traditional methods flaserin the future.
As we navigate the digital age, 3D printing stands as a beacon of ingenuity, shaping a world where imagination knows no bounds, and where ideas can seamlessly transition from the virtual realm to tangible reality.