Welcome to Print Chomp: Your Go-To Source for 3D Printed Meat
Originally posted on December 1, 2023 @ 12:38 pm
We are a technology blog committed to offering helpful pointers, thorough tutorials, and objective evaluations based on extensive testing and investigation. Whether you’re a curious food lover, health-conscious person, or fascinated by the latest advancements in food, we have you covered with our coverage of 3D printed meat.
3D printed meat, also known as 3D meat or 3D printed food, is an exciting and sustainable alternative to traditional meat products. By utilizing cutting-edge 3D printing technology, we can create meat-like forms using cultured animal cells or plant-based ingredients. This innovative approach to food production opens up new possibilities for addressing the ever-growing demand for protein sources while minimizing the environmental impact of conventional meat production methods.
Key Takeaways:
- 3D printed meat is a type of cultured or created meat made using 3D printers and additive manufacturing techniques.
- It offers a sustainable and alternative protein source for those following vegan or vegetarian diets.
- 3D printed meat can be made using both plant-based ingredients and cultured animal cells.
- It has numerous health benefits and can be tailored to specific dietary requirements.
- However, production costs and regulatory oversight are still challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption.
What Is 3D Printed Meat and 3D Food?
3D printed meat, also known as 3D meat, is a revolutionary concept in the world of food production. It involves using 3D printing technology to create meat-like products using cultured animal cells or plant-based ingredients. The process of 3D printing involves layering the material to form a desired shape, resulting in products that closely resemble traditional meat. This innovative approach to food production offers a range of benefits, including sustainability, customization, and alternative protein sources.
3D food refers to the broader category of food products created using 3D printing technology. It encompasses not only 3D printed meat but also other types of foods, such as desserts, pasta, and snacks. The technology allows for precise control over the composition and structure of the printed food, opening up new possibilities for culinary creativity and customization. From intricate pastry designs to personalized nutrition, 3D food has the potential to transform the way we think about and consume food.
In addition to its unique production process, 3D printed meat and 3D food offer various advantages over traditional food production methods. For example, 3D printing technology allows for the production of food with precise nutritional profiles, catering to specific dietary needs and preferences. It also has the potential to reduce waste, as ingredients can be precisely measured and used efficiently. Furthermore, 3D printed meat and food can be produced using fewer resources, making them a more sustainable alternative in a world facing increasing food demand.
3D printed meat and food offer precise control over composition and structure, personalized nutrition, and reduced waste, making them a sustainable and innovative choice.

Table: Comparison of 3D Printed Meat and Traditional Meat
| Criteria | 3D Printed Meat | Traditional Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Taste and Texture | Can be customized | Natural, variable |
| Production Process | Additive manufacturing technology | Animal farming and slaughtering |
| Sustainability | Requires fewer resources | High resource consumption |
| Dietary Restrictions | Can cater to specific dietary needs | Limited options for certain diets |
Table: A comparison of 3D printed meat and traditional meat, showcasing the unique features and advantages of 3D printed meat.
As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for 3D printed meat and food are expanding. Researchers and food companies are exploring new ingredients, flavors, and applications of 3D printing technology in the culinary world. While there are still challenges to overcome, such as affordability and regulatory considerations, the potential of 3D printed meat and food to revolutionize the food industry is undeniable. Whether it’s providing alternative protein sources, reducing environmental impact, or offering personalized nutrition, 3D printed meat and food are poised to shape the future of food.
How Is 3D Printed Cultured Meat Made?
3D printed cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat, is a fascinating and innovative alternative to traditional meat production methods. This sustainable and ethical approach involves using animal stem cells that are cultivated in a bioreactor. The cells are then differentiated into muscle and fat cells, which are later printed using a 3D printer. The printed meat is incubated to allow the cells to grow and form the desired texture and taste. This technology eliminates the need for raising and slaughtering livestock, making it a more environmentally friendly and humane option.
The process of producing 3D printed cultured meat begins by extracting a small sample of animal cells, typically taken from a biopsy. These cells are then placed in a nutrient-rich culture medium that supports their growth. Over time, the cells multiply and form a cell line, which can be used to produce larger quantities of meat. The cell line is transferred into a bioreactor where the conditions are optimized to promote cell growth and development. This controlled environment allows the cells to differentiate into muscle and fat cells, mimicking the natural process of meat formation in animals.
Once the cell differentiation is complete, the muscle and fat cells are carefully layered and printed using a 3D printer. The printer deposits the cells in a precise pattern to create a complex and realistic meat-like structure. The printed meat is then incubated to encourage the cells to merge and create a cohesive piece of meat. During the incubation process, the cells continue to multiply and develop their characteristic flavors and textures. The result is a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional meat products.
Table: Comparison of Traditional Meat Production and 3D Printed Cultured Meat
| Traditional Meat Production | 3D Printed Cultured Meat | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, water pollution | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced land and water use |
| Animal Welfare | Animal farming and slaughter | No animals harmed or slaughtered |
| Resource Consumption | Large land area, water, and feed requirements | Less land, water, and feed required |
| Food Safety | Potential for contamination and foodborne illnesses | Controlled and sterile production environment |
3D printed cultured meat is a groundbreaking development that has the potential to revolutionize the food industry. It offers a sustainable and efficient way to produce meat without the negative environmental and ethical impacts associated with traditional meat production. While this technology is still in its early stages, ongoing research and development are paving the way for a future where 3D printed meat could become a mainstream and accessible option for consumers.
Is 3D-Printed Meat Vegan/Vegetarian?
When it comes to 3D-printed meat, the question of whether it is vegan or vegetarian depends on the ingredients used in the process. Some varieties of 3D-printed meat are made using plant-based ingredients, such as soy, pea protein, and beetroot, making them suitable for vegans and vegetarians. These plant-based alternatives are designed to mimic the taste and texture of real meat, providing a cruelty-free option for those who choose to avoid animal products.
On the other hand, there are also 3D-printed meats that are produced using cultured animal cells. While these meats are not derived from traditional livestock raising and slaughtering, they still involve the use of animal cells. As a result, they may not be considered vegan or vegetarian by some individuals who adhere to strict definitions of these dietary preferences.
It is important to note that the ethical acceptability of 3D-printed meat can vary among vegans and vegetarians. This is a topic that sparks debate and discussion within these communities. As of now, regulatory oversight for 3D-printed meat is limited, and there is no standard definition or certification for labeling these products as vegan or vegetarian. This lack of clarity further adds to the complexity of the issue.
Table: Comparison of 3D-Printed Meat Types
| 3D-Printed Meat Type | Ingredients | Vegan/Vegetarian |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based 3D-Printed Meat | Soy, pea protein, beetroot, etc. | Vegan/Vegetarian |
| Cultured Animal Cell 3D-Printed Meat | Animal cells | May not be considered vegan/vegetarian |
“3D-printed meat can be a game-changer in the world of alternative protein sources. However, the classification of these meats as vegan or vegetarian is still a subject of debate. It’s crucial for consumers to carefully examine the ingredients and make informed choices based on their personal beliefs and dietary preferences.”
In conclusion, 3D-printed meat can be both vegan and non-vegan, depending on the ingredients used in the production process. While plant-based options provide cruelty-free alternatives for vegans and vegetarians, meats produced using cultured animal cells may not align with strict definitions of these dietary preferences. The ethical acceptability and regulatory oversight of 3D-printed meat are still evolving, and further research and development are needed to provide clearer guidelines and label certifications for these innovative food products.
Is 3D Meat Healthy?
When it comes to the health benefits of 3D meat, the key lies in its nutritious content. Unlike traditionally raised livestock-based meats, 3D meat is made from plant-based ingredients or cultured cells, which makes it higher in nutritional value. It is packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins that are crucial for a well-balanced diet.
According to a recent study published in the Journal of Food Science and Technology, 3D meat has a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer, and other health conditions. It also offers the advantage of being customizable to cater to specific dietary requirements or health conditions. For example, 3D meat can be tailored to be low in cholesterol or high in certain nutrients, making it an ideal choice for individuals with specific health concerns.
Furthermore, 3D meat is typically free from unhealthy fats that are commonly found in traditional meat. This makes it a healthier option for those who are conscious of their cholesterol intake. With its nutritious content and lower risk of health issues, 3D meat can be a valuable addition to a balanced and healthy diet.

| Nutrient | Per 100g of 3D Meat | Per 100g of Traditional Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 18g | 15g |
| Fat | 4g | 8g |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 75mg |
| Vitamin C | 20mg | 1mg |
| Iron | 2.5mg | 1.2mg |
“3D meat provides an opportunity to enjoy a delicious and satisfying meal while reaping the benefits of a more nutritious and health-conscious diet.” – Dr. Sarah Davis, Nutrition Expert
3D Meat: The Expenses Involved
As exciting as the prospect of 3D printed meat sounds, it’s important to understand the expenses involved in this novel food production technology. While the concept of printing meat may seem futuristic, the current reality is that the production costs can be quite high.
One of the major expenses is the cost of 3D printers themselves. Commercial-grade 3D printers specially designed for printing food can be quite expensive, often costing thousands of dollars. This initial investment can be a significant barrier for individuals or small businesses looking to adopt 3D meat production.
Additionally, the filaments used in 3D printers for printing meat require extensive processing to ensure they are safe for consumption. This processing adds to the overall production costs and can further contribute to the affordability challenge.
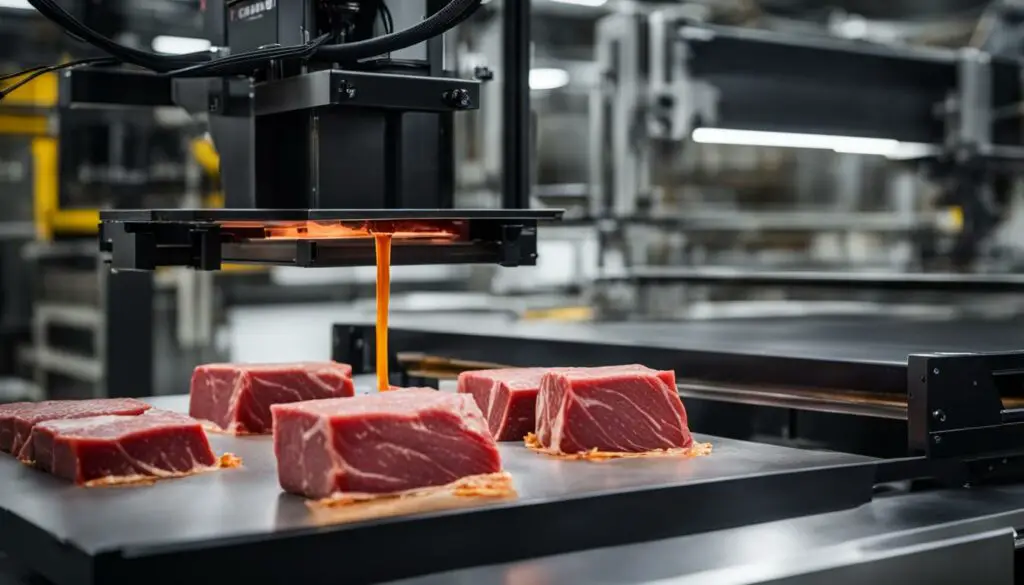

Moreover, learning how to handle and operate these 3D printers properly can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Without proper training, there is a risk of safety hazards and machine troubles, which can result in additional costs for maintenance and repairs.
To make 3D-printed meat more accessible and cost-effective, improvements in affordability and production requirements are necessary. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see advancements that address these challenges and make 3D meat production more attainable for various enterprises and consumers worldwide.
Is 3D Meat Eco-Friendly?
When it comes to sustainability and environmental impact, 3D meat is a promising alternative to traditional meat production methods. The 3D printing process used to create meat requires fewer resources and has a lower overall environmental footprint compared to raising livestock and processing meat. This makes it an eco-friendly choice for those concerned about the planet.
By eliminating the need for animal agriculture, 3D meat production helps reduce deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions associated with livestock farming. Additionally, the process uses significantly less water and land, making it more efficient and sustainable. These environmental benefits are further enhanced by the fact that 3D printing allows for the use of meat by-products, reducing waste in the food industry.
While 3D meat shows great promise in terms of sustainability, there is still work to be done to make the process more affordable and scalable. Currently, the production costs of 3D-printed meat can be high, and commercial-grade 3D printers used in the process are expensive. However, as technology advances and becomes more accessible, it is expected that these costs will decrease, making 3D meat a viable and eco-friendly option for the future of food.
In conclusion, 3D meat offers a sustainable alternative to traditional meat production practices. Its eco-friendly nature, coupled with its potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and deforestation, makes it an attractive option for those seeking to reduce their environmental impact. While there are still challenges to overcome, such as the affordability and scalability of the technology, 3D meat has the potential to play a significant role in creating a more sustainable and ethical food industry.
Conclusion
3D printed meat is not just a glimpse into the future; it is already transforming the way we think about food production. This innovative technology is paving the way for a more sustainable and ethical food industry, offering meat substitutes and reducing the environmental impact of traditional meat production.
With 3D printed meat, we have the potential to address the growing demand for protein while minimizing the use of resources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This disruptive technology has the power to revolutionize the food industry and provide a viable solution to the challenges we face in feeding a growing global population.
As we look to the future, 3D printed meat holds immense promise. With further research and development, we can overcome the current challenges of high production costs, regulatory oversight, and consumer acceptance. This means that, one day, 3D printed meat could become a staple in sustainable food production, offering a viable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional meat.
As consumers, we have the opportunity to embrace this innovative food technology and contribute to a more sustainable future. By exploring the potential of 3D printed meat and supporting its development, we can make a positive impact and shape the future of food for generations to come.
FAQ
What is 3D printed meat?
3D printed meat, also known as 3D meat or 3D printed food, is a type of cultured or created meat made using 3D printers and additive manufacturing techniques.
How is 3D printed meat made?
3D printed meat is made by feeding a 3D printer with cultured animal cells or plant-based ingredients and printing them into meat-like forms using layering techniques.
Is 3D printed meat vegan or vegetarian?
3D printed meat can be both vegan and non-vegan, depending on the ingredients used. Some are made using plant-based ingredients, while others are made using cultured animal cells.
What are the health benefits of 3D printed meat?
3D printed meat has a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, certain types of cancer, and other health conditions. It is typically higher in nutritional value and can be tailored to specific dietary requirements.
How much does 3D printed meat production cost?
3D printing meat can involve high production costs due to expensive printers and extensive processing of filaments. Improvements in affordability and production requirements are necessary for wider accessibility.
Is 3D printed meat eco-friendly?
Yes, 3D printed meat is considered eco-friendly as it uses fewer resources, reduces environmental impact, and eliminates the need for traditional livestock raising and processing.
What is the future of 3D printed meat?
3D printed meat offers a sustainable alternative to traditional meat production and has the potential to reshape the future of food. With further research and development, it can contribute to a more sustainable and ethical food industry.








