The Debate Over Cheapest 3D Printer: What You Should Know
Originally posted on December 3, 2023 @ 11:03 am
In this piece, we explore the topic of 3D printing and the continuing discussion surrounding the most economical 3D printer choices currently on the market. Whether you are a leisurely maker, business owner, or an expert in the field, comprehending the details of budget-friendly 3D printing devices is essential. Let us examine the advantages and disadvantages of various inexpensive 3D printers, their influence on the economy, and the important factors to consider before buying.
3D printing has revolutionized various industries, offering flexible design options, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective production. However, it’s essential to consider both the benefits and limitations of these machines. From restricted build sizes to copyright concerns, we’ll address the key aspects of the debate. As the manufacturing industry undergoes a transformation, 3D printing plays a significant role in shaping its future.
Key Takeaways:
- Cheapest 3D printers offer flexible design options, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective production.
- There are limitations in available materials and restricted build sizes for inexpensive 3D printers.
- The impact of 3D printing on the economy includes entrepreneurship opportunities and potential job transformation.
- Understanding the basics of 3D printing and how it works is crucial before making a purchase decision.
- 3D printing is not a Star Trek replicator, but it has advanced applications in various industries.
The Advantages of 3D Printing
3D printing offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive option in various industries. Whether you’re a designer, engineer, or entrepreneur, the flexibility and efficiency of 3D printing can revolutionize your workflow. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Flexible Design Options
With 3D printing, you have the freedom to create complex and intricate designs that may not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods. This technology allows you to bring your imagination to life, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Rapid Prototyping
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is the ability to quickly produce prototypes. Traditional prototyping methods often involve lengthy lead times and high costs. With 3D printing, you can iterate and refine your designs at a much faster pace, saving both time and money.
Print on Demand
3D printing enables on-demand production, eliminating the need for large inventories. You can create physical objects only when they are needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing waste. This also allows for customization and personalization, catering to specific customer requirements.
Strong and Lightweight Parts
3D printed parts can be designed to be both strong and lightweight, making them ideal for applications that require high strength-to-weight ratios. This is especially valuable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and robotics, where weight reduction is crucial for performance and efficiency.
Fast Design and Production
3D printing enables rapid design and production cycles. Since the process eliminates the need for tooling and manual labor, you can go from concept to final product in a fraction of the time compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This agility gives you a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
Minimizing Waste
Traditional manufacturing processes often result in significant material waste. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing method that only uses the necessary amount of material, minimizing waste generation. This not only reduces costs but also has a positive environmental impact by conserving resources.
Cost-Effective
3D printing can be a cost-effective solution, especially for small-scale production runs. It eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds, making it more affordable for prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. The ability to print on demand also reduces the costs associated with inventory management.
Ease of Access
Advancements in 3D printing technology have made it more accessible than ever before. There are now affordable desktop 3D printers available for personal use, as well as online 3D printing services that allow you to upload your designs and have them printed and delivered to your doorstep. This level of accessibility empowers individuals and small businesses to bring their ideas to life.
Environmentally Friendly
3D printing has the potential to reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. By minimizing material waste, optimizing designs for lightweight structures, and reducing the energy required for production, 3D printing contributes to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to manufacturing.
Advanced Healthcare Applications
3D printing has revolutionized the healthcare industry, enabling the production of custom medical devices, prosthetics, and even human organs. This technology has the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce surgical risks, and enhance the efficiency of medical interventions. The possibilities are truly groundbreaking.
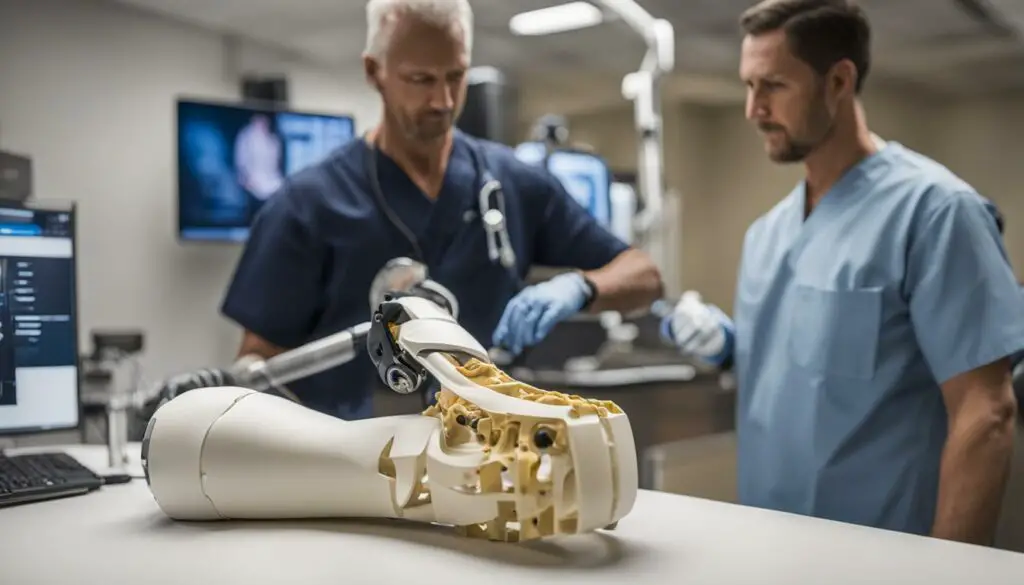
In conclusion,
3D printing offers a range of advantages, from flexible design options and rapid prototyping to cost-effectiveness and advanced healthcare applications. It has the potential to transform industries and open up new possibilities for innovation. However, it’s important to note that 3D printing also has its limitations, such as restricted build sizes and material availability. Understanding the benefits and limitations of this technology is crucial for harnessing its full potential.
The Disadvantages of 3D Printing
While 3D printing has many advantages, it also has its fair share of disadvantages that need to be considered. These limitations can impact the feasibility and effectiveness of using 3D printing technology in certain scenarios.
One major disadvantage of 3D printing is the limited range of materials that can be used. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that have a wide variety of materials to choose from, 3D printers are typically restricted to specific types of plastics or metals. This can hinder the production of certain objects that require alternative materials or unique properties.
Another drawback of 3D printing is the restricted build size. Most consumer-grade 3D printers have a limited build volume, meaning they can only produce objects of a certain size. This can be problematic for larger-scale projects or when manufacturing components that require a larger build area.
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Post Processing | After printing, additional steps may be necessary to achieve the desired finish or remove support material. |
| Large Volumes | 3D printing may not be cost-effective for producing objects in large quantities due to factors such as print time and material costs. |
| Part Structure | Objects created with 3D printing may have structural weaknesses or inconsistencies that affect their durability and performance. |
| Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs | As 3D printing technology advances, there is a concern that it may lead to a decrease in traditional manufacturing jobs. |
| Design Inaccuracies | Depending on the complexity of the design and the printer used, 3D printed objects may not always achieve the desired level of accuracy and precision. |
| Copyright Issues | The accessibility of 3D printing raises concerns about copyright infringement, as it becomes easier for individuals to reproduce copyrighted designs. |
These disadvantages highlight the importance of carefully evaluating the suitability of 3D printing for specific applications. While the technology continues to evolve and improve, it is crucial to consider these limitations when deciding whether to adopt 3D printing in various industries.
The Impact of 3D Printing on the Economy
3D printing is not just a technological advancement; it is part of a larger movement known as the maker movement. This movement encompasses individuals and communities who are empowered to create, innovate, and improve their local economies. By embracing 3D printing, you have the opportunity to become a part of this movement and contribute to the growth of your community.
One of the key impacts of 3D printing on the economy is its ability to support entrepreneurship. With lower barriers to entry and the availability of affordable 3D printers, aspiring entrepreneurs can turn their ideas into reality. The ability to create lower-cost prototypes allows entrepreneurs to test their products and refine their designs without incurring significant expenses. This enables them to bring their products to market faster and with reduced financial risk.
In addition to supporting entrepreneurship, 3D printing also has implications for manufacturing jobs. While there may be a reduction in traditional manufacturing jobs as a result of the adoption of 3D printing, new opportunities arise through skill transferability. As the demand for 3D printing grows, there will be an increasing need for skilled technicians and designers who can operate and optimize these technologies. This shift in the job market provides the chance for economic growth and the development of new industries.
| Benefits of 3D Printing in the Economy | Implications for |
|---|---|
| Lower cost prototypes | Entrepreneurship |
| Short-run manufacturing | Manufacturing Jobs |
| Digital supply chain | Local Economies |
3D printing has the potential to transform traditional manufacturing processes by enabling short-run manufacturing. This means that companies can produce smaller quantities of products without the need for expensive tooling or setup costs. This flexibility allows for more agile production and reduces the risks associated with holding large inventories. Additionally, 3D printing enables the creation of a digital supply chain, where products can be produced on-demand and delivered digitally, minimizing the need for physical inventory and reducing transportation costs.
The impact of 3D printing on the economy goes beyond cost savings and job creation. It has the potential to revolutionize the way products are designed, manufactured, and distributed. By embracing this technology, you can position yourself at the forefront of innovation and contribute to the growth and development of your local economy.
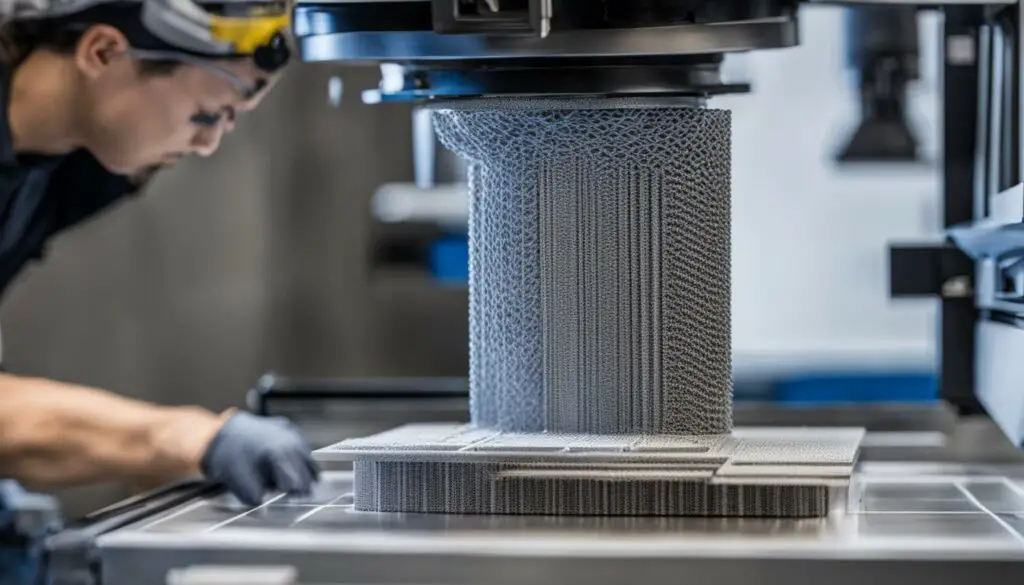

Additive Manufacturing Technologies
| Technology | Process | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Fused-deposition modeling (FDM) | Extrudes plastic filament layer by layer | Plastic |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Solidifies liquid resin layer by layer with light | Resin |
“Additive manufacturing allows for precise control over the design and production process, enabling the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or even impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.”
The layer-by-layer approach of additive manufacturing offers several benefits. It allows for the creation of intricate and complex designs that would be challenging to produce using traditional manufacturing techniques. Additionally, additive manufacturing offers greater design freedom, enabling the production of customized products tailored to specific requirements.
By understanding how additive manufacturing works, you can appreciate its versatility and potential applications across various industries. From rapid prototyping to manufacturing end-use parts, additive manufacturing is reshaping the way we create objects.
What 3D Printing is Not
Despite the imaginative portrayal of 3D printers as Star Trek replicators, it’s important to understand that they have limitations and design constraints. While 3D printing offers numerous benefits and possibilities, it cannot instantly create any desired object like those depicted in science fiction.
One of the key limitations of 3D printing is the restriction on available materials. While it is possible to print objects using a variety of plastics, metals, and composite materials, the range of options is not unlimited. Certain materials may not be suitable for 3D printing due to their properties or limitations of current technology.
Additionally, 3D printing is constrained by the size of the objects that can be printed. Most consumer-grade 3D printers have a build volume that limits the size of the objects that can be produced. Printing larger objects may require specialized equipment or may not be feasible at all.
“While 3D printing offers incredible versatility, it is crucial to keep in mind its limitations and design constraints.”
In summary, while 3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing and design processes, it is important to recognize that it is not a magical solution capable of instantly creating any object. Understanding the limitations and design constraints of 3D printing is essential for effectively utilizing this technology in various industries and applications.
Table: Comparing 3D Printing to Star Trek Replicators
| Feature | Star Trek Replicators | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Instant Creation | Objects are instantly created on-demand. | Objects are produced layer by layer, which takes time. |
| Material Variety | Can create objects from any material, including food. | Material options are limited to compatible plastics, metals, and composite materials. |
| Object Size | Capable of creating objects of any size. | Limited by the size of the 3D printer’s build volume. |
| Complexity | Can create highly complex objects with intricate details. | Complexity is limited by the layer-by-layer printing process. |
Conclusion
3D printing offers a range of benefits, making it an innovative and exciting technology. One of its key advantages is the ability to explore flexible design options and rapidly create prototypes. By enabling faster iterations, 3D printing can significantly reduce the time it takes to bring a product to market. This not only accelerates innovation but also allows for more efficient design processes.
Moreover, 3D printing has the potential to lower costs and revolutionize traditional manufacturing processes. By using only the necessary amount of material, it minimizes waste and optimizes resource allocation. This cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to streamline their production and reduce expenses.
However, like any technology, 3D printing has its limitations. The available materials and the size of objects that can be printed are currently restricted. While advancements continue to be made, these limitations need to be considered when determining the feasibility of 3D printing for a particular project.
Nevertheless, the impact of 3D printing on the economy is significant. It fosters entrepreneurship by enabling individuals to turn their ideas into tangible products with relatively low upfront costs. Additionally, while some traditional manufacturing jobs may be replaced, new opportunities arise in areas such as design, maintenance, and operation of 3D printers. This technology has the potential to reshape industries and create novel business models.
In conclusion, while 3D printing is not quite a Star Trek replicator, its advancements and applications are undoubtedly shaping various industries and opening up new possibilities. Embracing its benefits, understanding its limitations, and leveraging its potential can lead to enhanced innovation and economic growth.
FAQ
What are the advantages of 3D printing?
3D printing offers flexible design options, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective production. It allows for the creation of complex designs, fast iterations through rapid prototyping, and print on demand to save space and costs. Furthermore, it enables the production of strong and lightweight parts, minimizes material wastage, and has advanced applications in the healthcare sector.
What are the limitations of 3D printing?
3D printing has limitations in terms of available materials, restricted build size, and the need for post-processing to achieve desired finishes. It may not be cost-effective for large volume production compared to traditional manufacturing methods like injection molding. Additionally, parts produced through 3D printing can have structural weaknesses or delamination issues, and there are potential job reduction and copyright concerns with its accessibility.
What impact does 3D printing have on the economy?
3D printing is part of the larger maker movement, which empowers individuals and improves local economies. It lowers the cost of prototypes, supports entrepreneurship, and enables short-run manufacturing. While there may be a reduction in manufacturing jobs, 3D printing also creates new opportunities through skill transferability. It can transform the traditional supply chain by reducing the need for physical inventory and enabling digital delivery.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is the process of creating physical objects from digital models. It is an additive manufacturing process, where layers of plastic or other materials are built up to create the final object. Different types of 3D printers exist, including fused-deposition modeling (FDM) and stereolithography (SLA), which use different source materials. While 3D printing primarily focuses on plastics, metal printing is also possible, albeit at a higher cost.
How does additive manufacturing work?
Additive manufacturing, including 3D printing, involves building objects layer by layer. The source material, such as plastic filament or liquid resin, is fed into a printer with a print head that moves along the X and Y axis to create patterns. These patterns form the layers of the final object. Fused-deposition modeling uses filament and extrudes it through an extruder nozzle, while stereolithography uses liquid resin and solidifies it with light.
What is 3D printing not capable of?
Despite popular imagination, 3D printers are not capable of instantly creating any desired object like Star Trek replicators. 3D printing has limitations and design constraints. It cannot create consumable items like food, and there are restrictions on available materials and object size. While 3D printing has its strengths, it is important to recognize its limitations.
What is the conclusion about 3D printing?
3D printing offers a range of benefits, including flexible design options and rapid prototyping. It has the potential to lower costs and transform manufacturing processes. However, it also has limitations in terms of available materials and object size. The impact on the economy is significant, with implications for entrepreneurship and job creation. While 3D printing is not a Star Trek replicator, its advancements and applications are shaping various industries and opening up new possibilities.